NuvaRing Birth Control Ring
The NuvaRing birth control ring is a popular choice for contraception because it is convenient and effective. But it comes with side effects that can include serious blood clots and heart conditions for some women who use it.
NuvaRing is the first vaginal birth control ring. Available only by prescription, this flexible plastic ring, about two inches in diameter, is placed in the vagina where it releases a continuous, low dose of hormones to prevent pregnancy. A NuvaRing is inserted for three weeks, after which it is removed and a new one can be inserted after a one-week interval.
In a 2022 clinical report in the European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, over 90% of women agreed or strongly agreed that the vaginal ring was easy to insert, and more than 97% stated it was comfortable or very comfortable.
The hormones in NuvaRing — estrogen (ethinyl estradiol) and progestin (etonogestrel) — prevent eggs from leaving the ovaries. As a secondary mechanism of birth control, they also create changes in cervical mucus, which makes it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus.
NuvaRing is a combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC), a class of drugs that includes birth control patches and pills. While patches must be replaced weekly and pills have to be taken daily, the once-a-month approach has made convenience a major marketing point for NuvaRing’s current manufacturer, Merck & Co., Inc.
NuvaRing Timeline
-
2001
Organon Biosciences receives FDA approval for NuvaRing
-
2007
Schering-Plough acquires Organon BioSciences for $14.4 billion
-
2009
Merck & Co. acquires Schering-Plough for $41.1 billion
-
2009
Merck & Co. reports $88.3 million in sales from NuvaRing
-
2016
Merck & Co. reports $777 million in annual sales of NuvaRing
How Effective Is NuvaRing at Preventing Pregnancy?
In 2016, 5% of U.S. women who used birth control reported using NuvaRing at some point. The Guttmacher Institute estimates 594,391 women were using it as their method of birth control in 2018.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines “perfect use” as when a birth control method is used “correctly and consistently as directed.” “Typical use” is defined as how effective a method is during actual use, including those times with it is used inconsistently or incorrectly.
The percentages are based on the number out of 100 women who became pregnant within the first year of using it as a birth control method. In other words, if 1,000 women all used NuvaRing perfectly for a full year, there would be only three unintended pregnancies. If 1,000 women used NuvaRing as they typically would use it, there would be 90 unintended pregnancies.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of NuvaRing?
It is important to discuss your complete medical history with your doctor before using NuvaRing. Medical conditions or other medications you are taking may cause increased risks.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and convenient | Incompatible or dangerous for women with certain medical conditions |
| Fewer hormonal effects than pill or patch | Increased risk of potentially fatal heart attack, stroke, and blood clots |
| Can lead to regular, lighter and shorter periods | Potential for bleeding between periods |
| Exact positioning is not needed for it to be effective | Possible nausea and vomiting |
| No need to be fitted by a doctor | May cause vaginal discharge, irritation, or infection |
| Discreet, no one may know you are using it | May cause breast tenderness |
| Since it is inserted once a month, it may allow for greater spontaneity | Can reduce libido in users |
NuvaRing Risks
The most serious side effects of NuvaRing include an increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and blood clots.
A 2012 study of 1.6 million women’s medical records covering a 10-year period found that those who used NuvaRing faced a “6.5 times increased risk of confirmed venous thrombosis compared with non-users of hormonal contraception.”
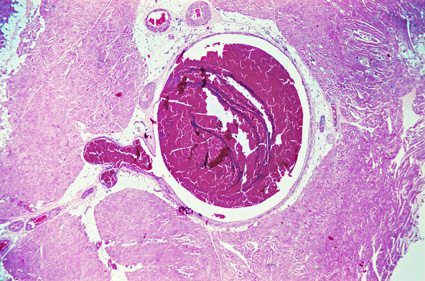
Venous thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in the veins, most often in the large veins of the legs, called a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). DVTs can be extremely painful, and if a clot breaks free, it can be fatal. The clot can travel to the lungs, block an artery, and cause a pulmonary embolism. DVT and PE are types of venous thromboembolism. VTE is the third-most frequently diagnosed vascular condition in America, behind heart attack and stroke.
In October 2011, the FDA released a study of more than 800,000 women that found an increased risk of venous thromboembolism among women using NuvaRing compared to oral CHCs.
While NuvaRing contains hormones comparable to birth control pills, as much as half of the hormones from pills are destroyed in the digestive tract, while the hormones from NuvaRing are absorbed directly into the body. NuvaRing uses a lower dose of hormones than pills, but the third-generation progestin (etonogestrel) in its formula has been linked to a higher clotting risk.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.

