Fosamax Side Effects
Fosamax (alendronic acid) is used to treat osteoporosis. Side effects include heartburn, upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea and constipation, as well as stomach, muscle, joint and bone pain. Rare and serious effects such as femur fractures and jaw problems (osteonecrosis of the jaw) have been reported.
Common Fosamax Side Effects
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea, diarrhea, constipation and cramping, according to Merck, the drug’s manufacturer. Studies show that side effects of Fosamax range from mild to severe.
Fosamax was introduced in 1995 to prevent age-related bone damage and other bone damaging diseases. However, people who are more susceptible to side effects from alendronate are the elderly, especially women who are more prone to developing osteoporosis.
- Heartburn
- Upset stomach
- Stomach pain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Bone, muscle or joint pain
- Bloating
- Gas
- Headache
- Changes in the ability to taste food
- Dizziness
Adverse reactions, such as bone, muscle or joint pain, affect about 4% of people who take Fosamax according to clinical trial data, but even those are rarely severe. The onset of side effects can sometimes occur after commencing treatment. Your doctor may advise you on how to prevent or mitigate some side effects.
Many side effects go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medication. And most stop immediately after discontinuing the medication. Some people can experience lingering effects for a day or so longer, but those also go away without the drug in their system.
Rare Serious Side Effects of Fosamax
The U.S Food and Drug Administration documented several of Fosamax’s serious side effects and subsequently distributed numerous warnings to highlight the potential dangers of Fosamax. Severe side effects include bloody stools, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, skin blisters, eye pain and swelling of the face, throat and tongue.
The drug’s medication insert warns it can lower blood calcium levels because the drug hinders the natural breakdown of bone. Long-term studies showed that calcium in the blood decreased about 2% in the first month of using Fosamax and suggested adding calcium and vitamin D as supplements.
- Itching or eye pain
- Sunlight sensitive rash
- Allergic reactions
- Severe musculoskeletal pain (joints, muscle, bone or jaw.
- Mouth ulcers
- Swelling in the face, tongue or throat
- Skin blisters
The FDA found that Fosamax patients can also develop intense bone, muscle and joint pains within days, months or years after starting the drug. For some people, this pain stops almost immediately after discontinuing the medication. For others, the side effects persist. Some side effects have led people to file Fosamax lawsuits against Merck.
Femur Fractures from Fosamax
Peer-reviewed research shows a connection between the long-term use of Fosamax and femur fractures. Some people reported unexplained aching in their thigh bones for weeks and months before experiencing unexplained breaks.
One meta-analysis of multiple studies concluded that people undergoing long-term treatment may be at an increased risk of an atypical femur fracture.
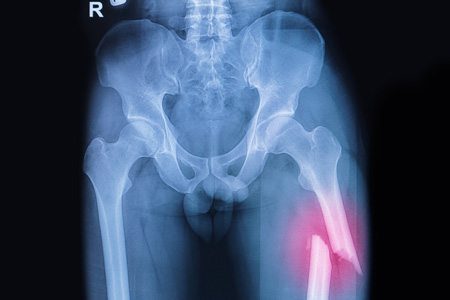
One review encouraged people with osteoporosis to have bisphosphonate therapy because rates of atypical femur fractures were 11 in 100,000. The rate of hip fractures decreased 20-50%.
Another study looked at 13 women with femur fractures from low levels of force and noted that nine had been taking alendronate, the generic form of Fosamax. Researchers said that the fractures may have occurred because alendronate stops the body from breaking down bone to create thick, but brittle bones.
One August 2022 study in Diabetes, Endocrinology & Metabolism Case Reports found that the risk of developing fractures persists long after stopping treatment with bisphosphonates such as Fosamax.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ)
The common use of bisphosphonates, including Fosamax, caused more awareness of the medication’s link to osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), a condition where gums don’t cover parts of the jawbone — mostly the mandible. Extensive dental surgeries like tooth extractions and teeth implants, oral infections, and conditions such as cancer, diabetes and kidney failure heighten the chances of jawbone death.
People who take 4 to 6 doses of Fosamax and similar drugs should expect unpredictable and inconsistent healing of their jawbone after an invasive oral procedure. Two separate studies documented the side effect, though rates varied in people who received bisphosphonates via an IV.
Merck’s clinical trials of Fosamax found a much lower incidence rate — 0.001% (1 in 100,000 people).
Esophagus Problems
A case-control study of U.S. military veterans shows an increased risk of Barrett’s esophagus and other esophageal problems with the use of Fosamax. Some people develop irritation, inflammation and bleeding ulcers in the esophagus, the tube that connects the mouth and stomach.
People with pre-existing upper gastrointestinal problems, such as Barrett’s esophagus, dysphagia, H. pylori infection or gastroesophageal disorder (GERD), should not take Fosamax.
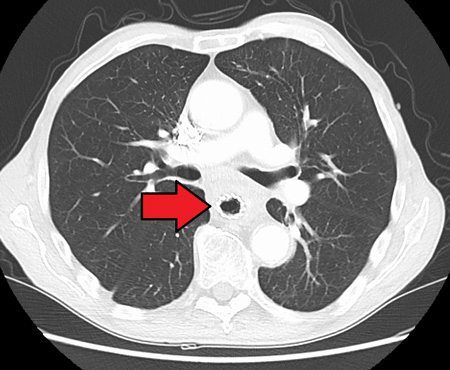
In some people, Fosamax leads to esophageal erosion with bleeding and esophageal perforation. Because of these potentially dangerous side effects, Merck recommends sitting upright or standing for 30 minutes after taking the drug with a full glass of water.
However, the FDA believes the benefits of oral bisphosphonate drugs, including Fosamax, outweigh their potential risks.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.


