Gadolinium Side Effects
Side effects of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) are usually mild and include injection site pain, nausea, itching, dizziness and headaches. Rare serious side effects such as gadolinium toxicity and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) can arise in people with severe kidney problems.
What Are Common Gadolinium Side Effects?
Burning pain, numbness or tingling, cognitive issues and kidney damage were commonly reported reactions in people presumed to have gadolinium toxicity.
According to Inside Radiology, vomiting occurs in less than 1 in 100 injections. And between 1 to 4 out of 100 people notice mild nausea or a headache.
A 2022 study into the awareness of gadolinium toxicity among non-radiologists in Saudi Arabia showed that 74.6% of participants had poor awareness, 20.9% had moderate awareness and only 4.6% understood the side effects.
- Altered taste
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Increased sweating
- Injection site pain
- Itching
- Nausea
- Oral discomfort
- Pins and needles sensation
- Rash
- Restlessness
- Shortness of breath
In 2018, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued new warnings that gadolinium can stay in the body for months or years after an MRI scan. A condition known as gadolinium retention happens when gadolinium builds up in bone, brain and kidney tissue.
Allergic Reactions to Gadolinium
Various allergic reactions are associated with exposure to GBCAs. Physicians classify reactions as mild, moderate or severe, but all are rare — occurring in 0.3% of cases, according to a BioMed Research International study.
- Altered taste
- Anxiety
- Cough
- Flushing
- Hives
- Itch
- Mild eye swelling
- Mild face swelling
- Nasal stuffiness
- Nausea
- Perspiration
- Rash
- Sneezing
- Vomiting
- Warmth
Moderate reactions include symptomatic tachycardia, dyspnea, symptomatic bradycardia, bronchospasm, hypotension and mild laryngeal edema. Severe reactions include severe respiratory distress, arrhythmia, convulsion, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, progressive angioedema, anaphylaxis and cardiopulmonary arrest.
Gadolinium Toxicity
Gadolinium toxicity is one of the side effects of GBCAs that can occur within hours after an MRI scan with one of these contrast agents. It can also manifest years later in people who have gadolinium buildup in their bodies.
Symptoms of gadolinium toxicity vary and range from mild to severe.
- Brain fog
- Burning or “pins and needles” sensations in the skin
- Changes to the skin, such as thickening or discoloration
- Difficulty breathing
- Flu-like symptoms
- Headache
- Metallic taste
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Pain in the bones or joints
- Vision or hearing changes
Medical providers consider approved GBCAs safe and well tolerated at recommended dosing levels. GBCAs are considered lanthanides, which are a group of metals that can be toxic.
During MRI scans where radio frequencies strike tissues in the presence of a magnetic field, free gadolinium can release into the tissues and bloodstream, resulting in toxicity. That affects people differently.
Causes and People at Risk of Toxicity
There are two classes of GBCAs: linear agents and macrocyclic agents. Multiple studies show that the brain holds onto more gadolinium particles from linear agents than macrocyclic agents. (Both leave some gadolinium behind). Research also suggests that skin and bones retain 100 times more than the brain.
People who have had multiple MRIs with GBCAs have a greater likelihood of toxicity. Additionally, pregnant women, children and people with kidney problems and inflammatory conditions are at higher risk.
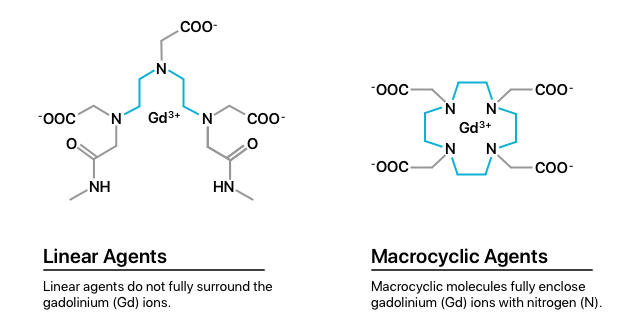
Early studies show that most macrocyclic molecules filter through the kidneys and leave the body within 24 hours after an MRI. The rest exit the body within 72 hours. However, more recent research shows less defined long-term retention of gadolinium.
Testing and Treating Gadolinium Toxicity
Few doctors understand gadolinium toxicity. And there are limited tests beyond blood and urine tests. Additionally, scientists have trouble developing a reliable monitoring system without defined normal ranges of gadolinium from each GBCA.
Chelation is a treatment that helps remove toxic heavy metals from the body, although its use isn’t well documented for gadolinium toxicity. During chelation, doctors give patients “chelating agents,” which bind gadolinium and filter it out of the body through the kidneys.
Healthcare providers may administer chelating agents through an IV, a pill, or as a rectal or sublingual suppository. In addition, because gadolinium toxicity causes pain in the bones, skin and joints, some people take pain-relieving medication as part of treatment.
Others may respond to immune system modulation treatment, which weakens the immune system through drugs or other agents. However, more testing is needed here, too.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF)
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis (NSF) is a disease that hardens and thickens the skin and internal organs, potentially leading to death. Exposure to GBCAs, either through an MRI or some other procedure, is responsible for almost every case of NSF.
NSF is a rare but serious side effect of GBCAs. The risk of developing NSF rises with increased linear gadolinium exposure.
GBCA drugs carry a boxed warning about NSF risk for people with kidney problems. About 4% of people with severe kidney problems develop NSF after exposure to GBCAs, and NSF is fatal about 30% of the time.
Gadolinium Deposition Disease (GDD)
Gadolinium Deposition Disease (GDD) is a newer condition that resembles NSF. Symptoms of GDD include brain fog, distal paresthesia (abnormal skin sensations), fatigue, headache, muscle twitching and insomnia.
Scientists believe GDD occurs in people with a genetic abnormality that impairs their ability to filter out heavy metals despite seemingly normal kidney function. Gadolinium lawsuits represent people with normal or near-normal kidney function who developed toxicity symptoms after injection with a gadolinium-based contrast agent.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.