Valsartan vs. Losartan: Key Differences and Similarities
Valsartan and losartan are generic blood pressure medications that lower blood pressure and treat heart failure. They both belong to the drug class called angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB). They work by inhibiting angiotensin II from tightening blood vessels. An ARB widens the blood vessels so the blood can move easier and lower blood pressure.

The main difference between valsartan and losartan is that valsartan has 24 hours of activity in the body at any dosage, whereas losartan will have a shorter duration of activity at a lower dosage.
Valsartan and losartan also have different side effects and can be used for other diagnoses. Keep reading to learn more differences between valsartan and losartan.
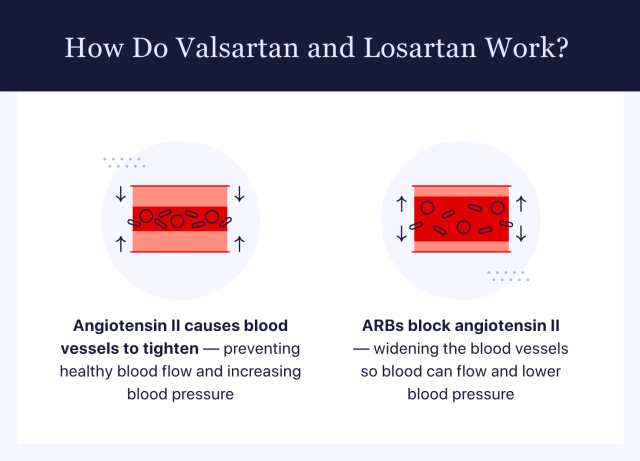
What Are the Differences Between Valsartan and Losartan?
| Valsartan | Losartan | |
|---|---|---|
| Drug class | Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) | Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) |
| Brand/generic available? | Brand and generic version available | Brand and generic version available |
| Brand name | Diovan | Cozaar |
| Form of drug | Oral tablet | Oral tablet |
| Standard dosage | 40 to 320 mg once daily | 50 mg once daily |
| Who uses this treatment? | Children and adults ages six and older | Children and adults ages six and older |
| Length of treatment | Long term | Long term |
Both valsartan and losartan are similar in that they can lower blood pressure. However, they do have slight differences in doses, how they are used for other diagnoses and side effects.
Active Ingredients and Metabolism of Valsartan and Losartan
Both losartan and valsartan contain active ingredients. The specific title of the active ingredient in losartan is losartan potassium. Losartan is a prodrug, an inactive compound that metabolizes (or converts) into its active form in the liver of the body. The metabolite, the active form, reduces blood pressure and peaks in activity levels around three to four hours.
Valsartan isn’t a prodrug and does not convert into an active metabolite like losartan; valsartan is the active compound. Valsartan peaks in levels around two to four hours, and the antihypertensive effects last around 24 hours.
Strengths and Dosage
Doses for valsartan and losartan will depend on the diagnosis and the patient’s age. It’s best to consult with your doctor on the right dosage to start with, especially when you are actively using other medications.
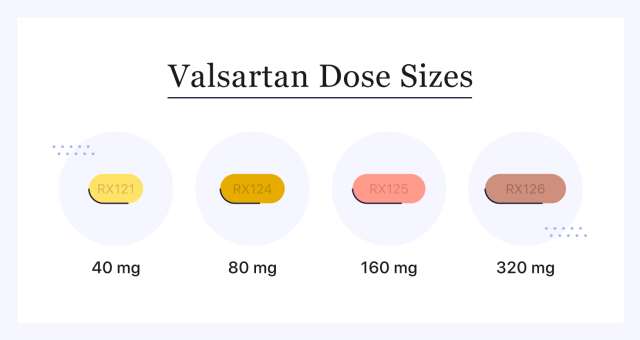
Valsartan comes in four dose strengths: 40 mg, 80 mg, 160 mg and 320 mg. For adult hypertension, your health care provider will likely prescribe either 80 mg or 160 mg daily to start. This dosage may be adjusted once consistently taken daily. The dosage isn’t typically adjusted for those with liver issues.
Below are more specific dosage recommendations for valsartan based on the diagnosis.
- Heart failure:
- 20-40 mg twice daily to start. Your doctor may adjust the dose to between 20 mg and the target dose of 160 mg twice daily.
- Post-heart attack:
- 20 mg twice daily to start. Your doctor may adjust the dose up to 160 mg twice daily. The goal dosage is 160 mg twice daily.
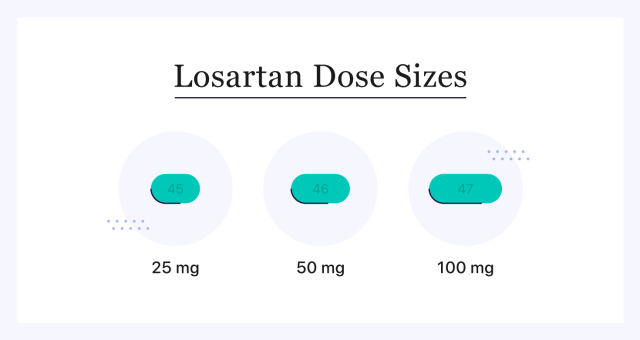
Losartan comes in three dose strengths: 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg. For adult hypertension, your health care provider will likely prescribe 25-50 mg daily to start. This dosage may be adjusted after taking it consistently. Those with liver issues may have a lower dosage to start.
Below are more specific dosage recommendations for losartan based on the diagnosis.
- Heart failure:
- 25-50 mg once daily to start. Your doctor may adjust the dose based on your blood pressure response with the target dose being 150 mg.
- Post-heart attack:
- 25-50 mg once daily to start. Your doctor may adjust the dose up to 100 mg daily. When taking valsartan or losartan, follow the instructions on the medication label or your doctor’s orders. If your current dosage isn’t the same as the ones above, do not change it before consulting your doctor.
Conditions of Valsartan and Losartan
Both valsartan and losartan are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hypertension in adults and children 6 years of age or older. However, they do have slight differences in other diagnoses they can treat.
| Valsartan | Losartan | |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | Yes | Yes |
| Hypertension with left ventricular hypertrophy | Off-label | Yes |
| Heart failure | Yes | Off-label |
| Post-heart attack | Yes | Off-label |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Off-label | Yes |
Valsartan can not only treat hypertension, but it can also treat heart failure and reduce the chance of death after a heart attack occurs.
Losartan can be used to treat diabetic nephropathy, which is found in those with hypertension and/or type 2 diabetes. Losartan is also used to reduce the risk of a stroke for those with hypertension with left ventricular hypertrophy.
Side Effects of Valsartan and Losartan
- Back pain
- Dizziness
- Nasal congestion
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- Abdominal pain
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Joint pain
| Valsartan | Losartan | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side Effect | Applicable? | Frequency | Applicable? | Frequency |
| Cough | Yes | N/A | Yes | 17% |
| Fatigue | Yes | 2% | Yes | 4% |
| Dizziness | Yes | 17% | Yes | 3% |
| Abdominal pain | Yes | 2% | Yes | N/A |
| Nasal congestion | No | - | Yes | 2% |
| Joint pain | Yes | 3% | Yes | N/A |
| Back pain | Yes | 3% | Yes | 2% |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | Yes | 3% | Yes | 8% |
| Diarrhea | Yes | 5% | Yes | 4% |
- Abdominal pain
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Viral infections
- Cough
- Back pain
- Diarrhea
Drug Interactions
Both valsartan and losartan interact with the same drug type. There are a few things you want to keep in mind when understanding drug interactions with either valsartan or losartan.
- Potassium levels should be monitored when taking potassium supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics or salt substitutes containing potassium along with an ARB. There’s an increase in risk for hyperkalemia — high levels of potassium in the blood.
- There’s an increased risk of kidney issues when taking an ARB with an NSAID. Kidney function should be monitored when taking an ARB and NSAID.
- There’s an increased risk of lithium toxicity when taking an ARB with lithium. Monitor lithium levels when taking an ARB and lithium.
- There’s an increased risk of severely low blood pressure, kidney issues and hyperkalemia when taking an ARB with ACE inhibitors, aliskiren or other ARBs.
Below is a comprehensive list of drug interactions with losartan and valsartan.
| Drug | Drug Class | Valsartan | Losartan |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium chloride Potassium citrate | Potassium supplements | Yes | Yes |
| Avapro (irbesartan) Atacand (candesartan) Micardis (telmisartan) | ARBs | Yes | Yes |
| Aldactone (spironolactone) Dyrenium (triamterene) Midamor (amiloride) | Potassium-sparing diuretics | Yes | Yes |
| Advil (naproxen) Motrin (ibuprofen) | NSAIDs | Yes | Yes |
| Cataflam (diclofenac) | |||
| Salt substitutes containing potassium | N/A | Yes | Yes |
| Zestril (lisinopril) Capoten (captopril) Lotensin (benazepril) | ACE inhibitors | Yes | Yes |
| Eskalith (lithium) | Antimanic agents | Yes | Yes |
Valsartan vs. Losartan FAQ
Below are commonly asked questions about valsartan, losartan and the drugs’ uses.
Is Valsartan or Losartan More Effective?
A 2001 study found valsartan and losartan are similarly effective in reducing blood pressure, specifically in patients with mild to moderate hypertension. In the study, losartan was seen with a decrease in serum uric acid levels, whereas valsartan was not.
There are studies that show that valsartan at doses of 160 mg and 320 mg are more effective in reducing blood pressure than losartan at doses of 100 mg.
Can You Use Valsartan or Losartan When Pregnant?
It’s not recommended to use valsartan or losartan during a pregnancy. If taken while pregnant, valsartan can lower the amount of the fluid around the baby, especially during the second and third trimesters. The reduced fluid can lead to long-term damage to the baby’s kidneys and lungs.
“Valsartan and losartan shouldn’t be taken past 12 weeks of pregnancy. It’s recommended to use a form of contraception while taking either drugs.”
Valsartan and losartan shouldn’t be taken past 12 weeks of pregnancy. It’s recommended to use a form of contraception while taking either drug. Your doctor can recommend alternatives to valsartan or losartan that are safe to use during pregnancy.
Can You Use Valsartan or Losartan When Breastfeeding?
There are no reputable studies that focus on the risk of using valsartan or losartan while breastfeeding. Discuss with your health care provider the benefits and risks of using this medication while breastfeeding.
Can You Use Valsartan or Losartan With Alcohol?
There’s the potential that drinking alcohol can increase blood pressure and lower the effects of the medications — making the user feel lightheaded or dizzy.
Avoid drinking alcohol the first couple of days of taking the medication to see how it affects you. You can also discuss with your health care provider their recommendations for drinking alcohol when taking the medication.
What Is a Good Replacement for Valsartan?
There are a variety of alternatives to valsartan if it isn’t available. Other than losartan, irbesartan is the ideal replacement for both valsartan and losartan. Your doctor may also choose to prescribe ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics or calcium channel antagonist drugs — depending on your specific treatment needs.
How Long Does Losartan Last?
A daily dose of losartan lasts 24 hours in the system, with an onset of action that takes six hours.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.

