Yaz
Yaz is a popular oral contraceptive pill that contains a combination of drospirenone and ethinyl estradiol. Side effects of Yaz include spotting, breast tenderness and headache. Yaz is not recommended for women with a history of headaches with aura, heart disease, blood clots or breast cancer.
What Is Yaz?
Yaz is an FDA-approved oral contraceptive that is also approved to treat premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) and acne. Women may take it on its own or in combination with other treatments to produce the desired effects.
Each Yaz pill contains 3 mg of drospirenone and 0.02 mg of ethinyl estradiol.


Yaz is not the same as two similar-sounding medications: Yasmin and Yasminelle. All three drugs are contraceptives, but Yasmin contains more ethinyl estradiol than Yaz. Yasminelle has the same amount of ethinyl estradiol as Yaz but contains three extra placebo pills in a month’s supply.
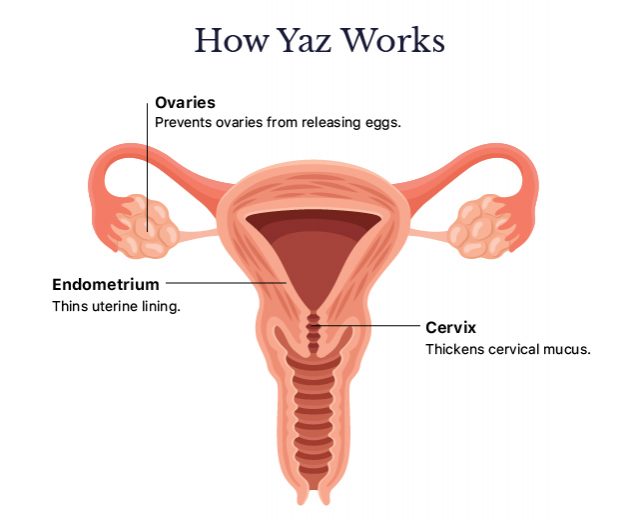
How Does Yaz Work?
Yaz prevents pregnancy in two ways. Hormones in the drug prevent your ovaries from releasing eggs. They also thicken your cervical mucus and thin your uterine lining, making it difficult for sperm to travel or for a fertilized egg to attach to your uterine wall.
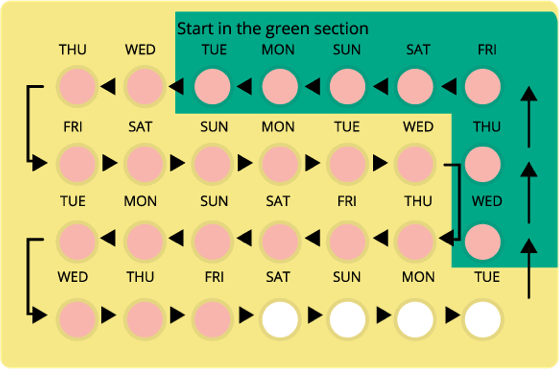
A month’s supply of Yaz contains 24 pink pills with hormones in them and four white placebo pills. While taking the placebo pills, you’ll get your period. Women may also opt to continue taking the pink pills uninterrupted, skipping the placebos and avoiding having a period.
How to Take Yaz Birth Control Pills
Women should take Yaz pills one at a time at the same time each day. Follow the order of the pills in the blister pack. If you choose to take the inactive white pills, only do so when you’ve completed all of the pink in the pack.
You can take Yaz pills with or without food. It’s best to take them after your evening meal or at bedtime with some liquid.
Missing an active dose of Yaz can reduce its effectiveness in preventing pregnancy. If you miss a dose, take the missed pill as soon as you remember.
Vomiting and severe diarrhea can also disrupt your body’s ability to absorb the drug. If you throw up three hours after taking Yaz, consider it a missed dose.
Daily Yaz Dosage
You can start taking Yaz on the first day of your period or the first Sunday after your period starts. Take one pink pill daily for 24 days and then one white pill for four days. The timing for taking Yaz can adjust if you change from one birth control pill or method to Yaz.
- Switching from a different birth control pill: Start taking Yaz on the same day that a new pack of your old pills would have started.
- Switching from a different birth control method: If switching from a transdermal patch, vaginal ring or injection, start Yaz when the next application or next dose would have been due. If switching from an intrauterine device or implant, start taking Yaz the day after removal.
- After pregnancy: Start taking Yaz no sooner than four weeks after giving birth to avoid an increased risk of blood clots. Do not take Yaz if you are currently pregnant or breastfeeding.
Yaz doesn’t become fully effective until you take it for at least seven days. Use an alternate form of birth control, such as condoms or contraceptive sponges, while Yaz builds to full strength.
What Are the Side Effects of Yaz?
The most common side effects of Yaz are spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods, breast tenderness, nausea and headache. These side effects are usually mild and often go away. Yaz is also less likely to make you gain weight compared to other birth control pills that are not formulated with drospirenone.
Yaz also carries a black box warning stating that women who smoke cigarettes while taking the drug have an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The risk is higher for women over the age of 35. Women who smoke should not take Yaz or any other oral contraceptive that contains estrogen.
Yaz Precautions
Yaz may not be the best birth control option for some women. Discuss your full medical history with your doctor before taking Yaz, especially any history of heart disease, blood clots or hormone-sensitive cancer. Taking Yaz could make these problems worse.
- Have preexisting kidney, liver or adrenal disease
- Are at high risk for arterial or venous thrombotic diseases
- Have ever had blood clots in your legs, lungs or eyes
- Have rhythm diseases of the heart such as arterial fibrillation
- Have ever had a stroke or heart attack
- Have or have had breast cancer or other estrogen- or progestin-sensitive cancer
- Have or have had cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice from other birth control pills
- Have uncontrolled high blood pressure
- Have diabetes with vascular disease
- Have migraine headaches with aura
- Are a heavy smoker aged 35 or older
- Take certain combinations of drugs for hepatitis C
- Have recently had major surgery requiring bed rest
- Are experiencing undiagnosed genital bleeding
- Are pregnant
Don’t take Yaz unless your doctor says it’s safe for you. If Yaz is not an option for you, ask your physician what type of birth control fits someone with your medical history.
As of 2022, women who have experienced rare, but serious adverse effects are filing Yaz lawsuits.
Yaz Interactions
Certain foods, drugs and supplements interact with Yaz and render it less effective or amplify its side effects. The medication’s absorption rate is slower when taken following high-fat meals
- Reduced Effectiveness: Phenytoin, carbamazepine, bosentan, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, topiramate, barbiturates and products containing St. John's wort may decrease the effectiveness of birth control pills like Yaz.
- Raising Yaz Levels: Grapefruit juice, vitamin C supplements and foods that are very high in vitamin C may raise the level of Yaz present in your bloodstream. This is true for most birth control pills.
- Decreasing Yaz Levels: Atorvastatin, acetaminophen, azole antifungals, verapamil, macrolides and diltiazem can also increase the amount of Yaz in the bloodstream.
- Increased Liver Enzymes: Taking hepatitis C drug combinations that include ombitasvir, paritaprevir or ritonavir at the same time as Yaz may result in increased liver enzymes.
- Increased Potassium Levels: Yaz may increase the amount of potassium in your blood. Women who take other drugs that can increase potassium levels should have their potassium monitored while on Yaz.
Discuss your diet and other medications with your doctor before taking Yaz. If you need to take medications with known interactions, your doctor may prescribe a different type of birth control for you.
Why Was Yaz Recalled?
Yaz’s manufacturer, Bayer, recalled approximately 33,000 boxes of Yazin 2009 because of incorrect specifications for the dose of drospirenone in the drug. Bayer had incorrectly claimed that the levels of drospirenone in its product fell within normal parameters.
Despite this controversy, the many Yaz settlements that were paid out and the introduction of generic competitors to the market, sales of Yaz still generate millions of dollars in revenue for Bayer. The drug is considered safe to take as long as your doctor reviews your medical history with you first.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.


