
Collagen
Collagen is a protein that provides building blocks for many of the body’s tissues, such as bones and skin. It allows tissues to stretch and be flexible. As people age, collagen production naturally decreases. Collagen supplements may have health benefits.
Get the Highest Quality Multi Collagen Powder
Highest Quality Multi Collagen Powder
NSF Certified for Sport ™
Advertisement
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is the most abundant protein found in the body. These proteins form a mesh of fibers that help provide support and flexibility to the body’s tissues and form key components that lead to healthy muscle, skin, bones and tendons.
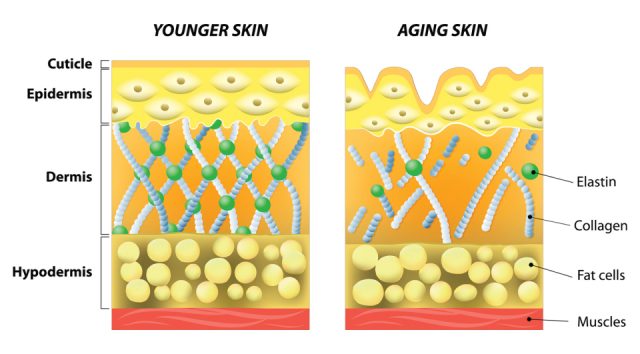
Researchers have identified at least 28 types of collagen. Those classified as type I, II and III, which are found in the skin, bones and blood vessels and organs, make up 80% to 90% of all collagens.
As you age, collagen production decreases and the body is less able to repair and replace it. This leads to less firm skin, weaker cartilage in joints and other changes. Because of this, collagen supplements have become popular.
Collagen vs. Collagen Peptides
When we eat protein-rich food, the body uses amino acids to make collagen. But collagen in its natural form is difficult to digest because it’s made of tightly packed, long fibers.
Most collagen supplements use smaller forms of collagen believed to be easier to digest. These are called collagen peptides or hydrolyzed collagen. Manufacturers apply chemicals or high heat to collagen to break it down into smaller pieces to produce collagen peptides.
What Does Collagen Do?
Collagen’s main role is to provide building blocks for body parts and to keep them strong and supple. Each type of collagen has different properties and functions differently.
- Type I: The most plentiful amount of collagen; made up of long, tightly packed fibers found in skin, ligaments, teeth, bones and tendons.
- Type II: Shorter fibers found in cartilages that form tough, flexible tissues in body parts such as the joints, ears and nose.
- Type III: Found in body parts such as blood vessels, intestines and skin; helps blood clot and wounds heal.
Like a rope of interwoven strands, each collagen fiber is composed of millions of proteins called peptides. All types of collagen help the body’s tissues maintain their shape, elasticity and strength.
What Are the Uses for Collagen?
Collagen naturally produced in the body is used for a diverse array of functions including supporting vision, hair growth and recovering from injuries. It’s believed that the broken down form of collagen found in collagen supplements is easily converted, broken down and absorbed into the body. This potentially makes it useful for several medical and cosmetic purposes.
Manufacturers source collagen from cows, chickens and fish for use in supplements and medical products. Scientists are also working on synthetic forms of collagen.
Medical
Collagen supplements may be useful in reconstructive, cosmetic and oral surgery. They can potentially help wounds and burns heal, promoting new tissue growth. Some people may use collagen supplements to decrease osteoarthritis symptoms.
Cosmetic
The natural properties of collagen make it appealing for cosmetic applications. Because it helps retain moisture, manufacturers add it to some skin creams and hair treatments. In cosmetic medicine, injected collagen fillers improve the quality and density of skin.
Benefits
Research results on the benefits of collagen supplements are mixed. Some studies have found supplements useful for increasing muscle mass and strength, alleviating arthritis pain and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Many of the studies reporting benefits are industry funded. More objective clinical trials are needed to evaluate the effectiveness of supplements.
Factors Affecting Collagen Production
Age is the number one factor that leads to decreased collagen production.People produce 1% less collagen in the skin each year after age 20, according to Suzan Obagi, assistant professor in dermatology at the University of Pittsburgh and director of the Cosmetic Surgery and Skin Health Center.
In addition to age, several other factors contribute to decreased collagen production as well.
- Smoking: This damages collagen and decreases the amount of oxygen that gets to the skin, making it difficult for tissues to regenerate.
- Diet: Eating diets high in processed meats and refined sugar can cause inflammation and collagen hardening and fragmentation.
- Sleep: Getting enough sleep is important because the body produces new cells and collagen during sleep.
- UV Rays: Too much exposure to ultraviolet light breaks down collagen and encourages skin cells to rebuild incorrectly, causing wrinkles.
- Health Conditions: Autoimmune disorders and connective tissues diseases cause inflammation and cause antibodies to attack collagen in the skin, joints and other body parts.
- Avoid Stress: Too much stress decreases collagen production.
Speak with your doctor about ways to help manage stress, support restful sleep and support in quitting smoking. Sunscreen and working with your healthcare team to manage health care conditions can also help improve overall health.
Can You Boost Collagen Production?
People may be able to help their bodies make more collagen, even if production naturally decreases with age. Collagen is found in a number of food sources. Many consumers are also interested in the possible benefits of supplements.
The science on collagen supplements isn’t very extensive or conclusive, but some studies have found promising results. Further study is needed to collect more data.
Natural Sources of Collagen
Natural sources of collagen include certain foods, though research hasn’t definitively proven that eating collagen directly can benefit the skin or joints because it breaks down when it’s digested.
A good way to support natural collagen production is to eat a healthy diet of foods rich in amino acids and nutrients.
- Animal bone broth made from simmering bones in water and a small amount of vinegar anywhere from 4 to 24 hours.
- High protein foods such as poultry, fish, meats, dairy, eggs, legumes and soy.
- Foods that contain zinc, such as nuts, whole grains, legumes and shellfish.
- Foods that contain vitamin C, including berries, citrus fruits, tomatoes, leafy greens and bell peppers.
- Sulfur-containing foods, such as broccoli, onions and garlic.
Collagen creams and injections may offer some benefits, although the science is mixed on their effectiveness. Additionally, collagen injections may prompt allergic reactions. Speak with your doctor about your medical history, including any allergies you may have before trying collagen products. Many contain ingredients that are common allergy triggers such as fish.
Synthetic Collagen
Because the chemical structure of collagen is so complex, scientists have had a difficult time recreating it. But researchers are getting closer to making synthetic collagens for biomedical applications that don’t come from animals or humans.
For example, scientists at Rice University have developed a synthetic collagen that could help wounds heal. Scientists at Emory University have developed shape-shifting collagen that may be used to control drug delivery and in tissue engineering.
Interested in Buying Multi Collagen Protein Powder?
CB Supplements offers the highest quality multi collagen powder that’s naturally formulated to keep your joints, skin, hair, nails and gut healthy.
- First and only multi collagen NSF Certified for Sport ™
- 5 types of collagen per scoop
- Gluten, dairy and grain-free
- Non-GMO and paleo-friendly
Advertisement
Collagen Supplements
Collagen supplements have grown in popularity for their possible ability to rejuvenate aging skin, increase muscle mass and lessen arthritis pain. But most researchers agree there isn’t enough high-quality evidence on whether or not these work, or how long collagen takes to work once supplements are taken.
Though the research shows promise, many of the studies come from collagen supplement manufacturers.
“We’re not actually sure if collagen supplements benefit us,” said Cedars Sinai dermatologist Dr. Ohara Aivaz. “The issue is that most things we ingest are broken down by stomach acids and are not absorbed into the bloodstream. It’s unclear if we absorb ingested collagen or if it’s totally broken down in the stomach.”
Safety is another issue because the U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulates collagen supplements as food rather than as medications, which means they’re subject to less strict standards than pharmaceuticals. Some experts are concerned supplements may contain heavy metals or other contaminants.
Supplements come from animal sources of collagen such as cows, fish or chickens. People can buy them in powders, liquids or capsules.
Calling this number connects you with a Drugwatch representative. We will direct you to one of our trusted legal partners for a free case review.
Drugwatch's trusted legal partners support the organization's mission to keep people safe from dangerous drugs and medical devices. For more information, visit our partners page.


